Tasks
A Task orchestrates different Instances via operations to result in a logical process flow. Such a Task does not need to describe who is going to transport an item - it is important that the item is transported.
Generally speaking a Task in LoTLan describes that a amount of items should be picked up at some location and be delivered to another location. A Task can optionally be triggered by an event, but it can also have follow up Task or be repeated. Even an event at the end of a task which is expected can be described.
Task {name}
Transport
From {transportOrderStep_pickup}
To {transportOrderStep_destination}
TriggeredBy {none|event|time}
OnDone {none|followUpTask}
FinishedBy {none|event|time}
Repeat {none = once|1, ..., n|0 = forever}
Constraints {none|constraint}
End
However, we start with some simple transportation tasks. To simplify this down in the following the simplest structure of a Task is build and later on extended with optional functionality. We also use these Locations and TransportOrderSteps not to inflate this page.
Location goodsPallet
name = "productionArea_palletPlace"
type = "pallet"
End
Location warehousePos1
name = "warehouseArea_pos1"
type = "pallet"
End
TransportOrderStep loadGoodsPallet
Location goodsPallet
FinishedBy agvLoadedAtGoodsPallet == False
End
TransportOrderStep unloadGoodsPallet
Location warehousePos1
FinishedBy agvLoadedAtWarehousePos1 == True
End
Example Simple Task
In the simplest form a Task in LoTLan just describes that an item should be picked up at some location and be delivered to another location:
Task transportGoodsPallet
Transport
From loadGoodsPallet
To unloadGoodsPallet
End
In terms of the introduced example production hall this Task looks like depicted in the following figure.
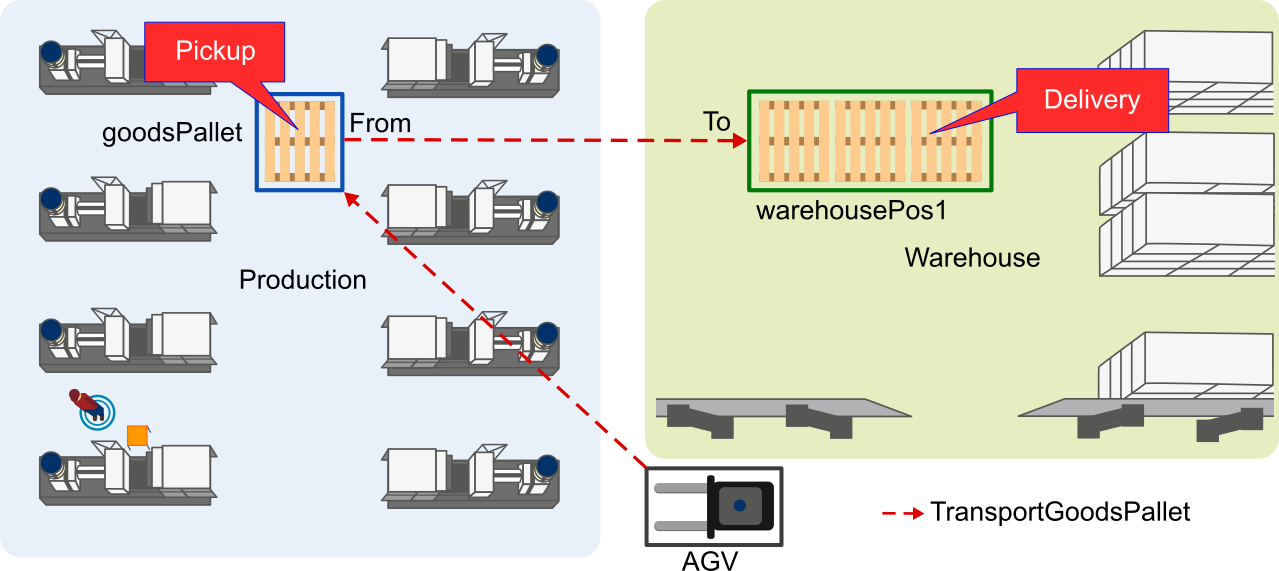 Figure 1: Floor plan with Task TransportGoodsPallet
Figure 1: Floor plan with Task TransportGoodsPallet
This Task transportGoodsPallet could be done by an AGV, that picks up a pallet from goodsPallet inside the production area and delivers it to the warehousePos1 in the warehouse area.
Example TriggeredBy Task
A Task can be extended with a TriggeredBy statement that activates that Task if the case occurs. This statement can be an event like a button press or be something simple as a specific time:
Event buttonPallet
name = "A_Unique_Name_for_a_Button"
type = "Boolean"
End
Task transportGoodsPallet_2
TriggeredBy buttonPallet == True
Transport
From loadGoodsPallet
To unloadGoodsPallet
End
In this example, the Task transportGoodsPallet_2 triggered by the event if the value is equal (== True).
In terms of the introduced example production hall this Task looks like depicted in the following figure.
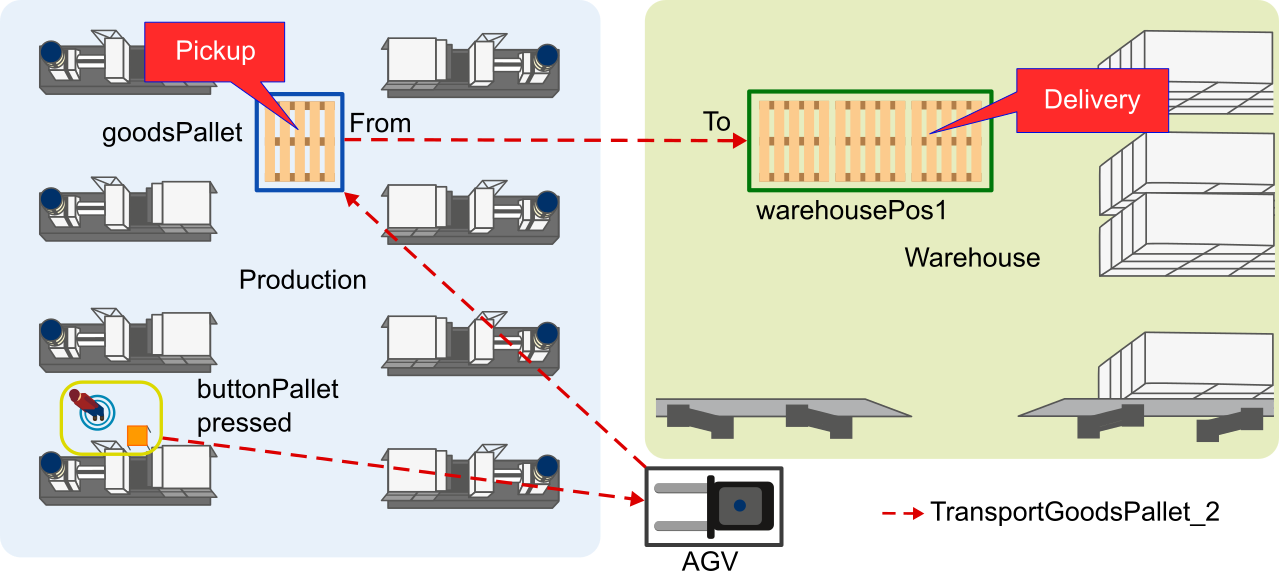 Figure 2: Floor plan with Task transportGoodsPallet_2
Figure 2: Floor plan with Task transportGoodsPallet_2
This Task transportGoodsPallet_2 could be done by an AGV, that picks up a pallet from goodsPallet inside the production area and delivers it to the warehousePos1 in the warehouse area, when the button buttonPallet is pressed.
Example OnDone Task
A Task can be extended with a OnDone statement that activates another Task when the original one has ended:
TransportOrderStep loadEmptyPallet
Location warehousePos1
FinishedBy agvLoadedAtWarehousePos1 == True
End
TransportOrderStep unloadEmptyPallet
Location goodsPallet
FinishedBy agvLoadedAtGoodsPallet == False
End
Task refill
Transport
From loadEmptyPallet
To unloadEmptyPallet
End
Task transportGoodsPallet_3
Transport
From loadGoodsPallet
To unloadGoodsPallet
TriggeredBy buttonPallet == True
OnDone refill
End
In this example another Task is introduced. This Task refill is the same transport as the formerly introduced transportGoodsPallet, just the other way around. On the other hand, transportGoodsPallet_3 here shows now the OnDone statement that points to refill an runs that Task if done. That means a concatenation of Tasks is allowed. Exploiting this behaviour infinite Tasks can be managed by pointing to each other. So refill could also point to transportGoodsPallet_3 in a OnDone statement.
In terms of the introduced example production hall this Task looks like depicted in the following figure.
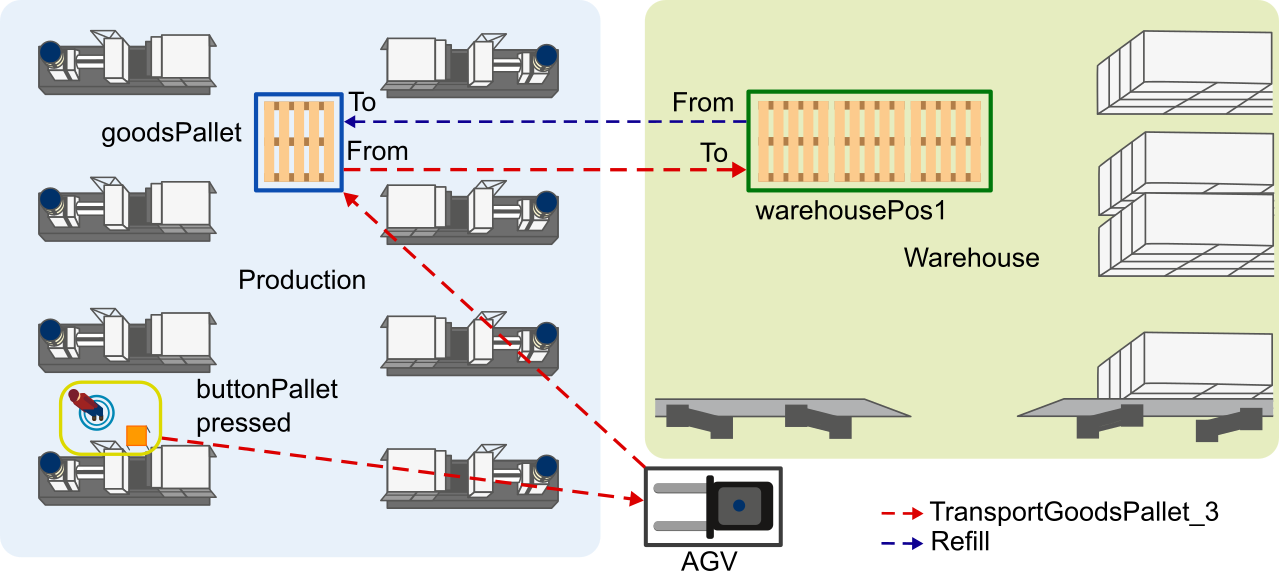 Figure 3: Floor plan with Task transportGoodsPallet_3 & refill
Figure 3: Floor plan with Task transportGoodsPallet_3 & refill
This Task transportGoodsPallet_3 could be done by an AGV, that picks up a pallet From goodsPallet inside the production area and delivers it To the warehousePos1 in the warehouse area, when the button buttonPallet is pressed. After that the AGV executes the Task refill and so, it picks up a empty pallet From the warehousePos1 and delivers it To the goodsPallet location.